Code Example
In above example int, float, char, String, boolean these are the data types, they tell which kind of value variables MyMark, Radius, FLetter, MyName, Is_found can store. In java variable are strongly typed for example, MyMark only can store int type value, FLetter only can store char type value etc.
Note That
- Data type represents the type of information that a variable can store.
- Date type restricts the type of information which a variable can store.
- Data type also represents memory size of the variable.
Why So many Data Types ..?
When we declare a variable with any data type then, it going to reserve a space in memory, here two things are very important to know.
- Type of Information (data type)
- Size of Information (Req. space to store)
Each type of data type reserve different – different size of space in memory ( RAM ), and they can store only that type of information which is their data type.
Since we have limited size of memory ( RAM ). As a programmer we should waste minimum memory, so we should use that data type in which memory wastage will be less, because of this reason many type of data types are created.
Types of Data Type
In Java data types are divided into two types
- Primitive data types
- Non - primitive data types
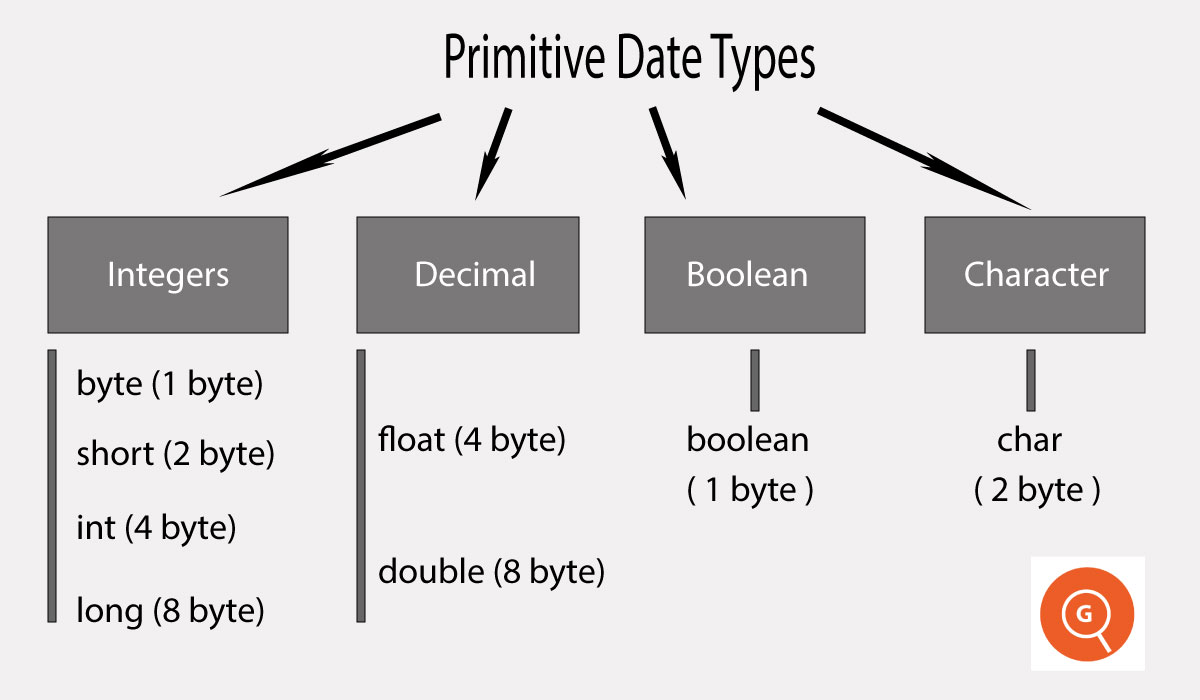
1. Primitive Data Types
Primitive data type are fixed size in nature means the variable with primitive data type is allocated a fixed size of memory and they do not contain any additional methods.
In java there are 8 primitive data types and all these are keywords. These are listed below.
| S.No |
Data Type |
Size |
Default Value |
| 1 |
byte |
1 byte |
0 |
| 2 |
short |
2 byte |
0 |
| 3 |
int |
4 byte |
0 |
| 4 |
long |
8 byte |
0 |
| 5 |
float |
4 byte |
0.0 |
| 6 |
double |
8 byte |
0.0 |
| 7 |
char |
2 byte |
Empty |
| 8 |
boolean |
1 byte |
false |
Integers (whole number)
Integers data type are used to store whole number (without decimal point), they can be either positive or negative for example ( 124,-8276, 32 ) etc.
- There are four data type which can be used to store an integer number, these are byte, short, int and long, we can choose any among from them based on our requirement.
- There are only difference of size in these four data types, let’s see in detail about each.
byte
We can use byte data type when we have to store integer number between -128 to 127, it take only 1 byte space to store number.
- Size: 1 byte
- Range: -128 to 127
- Suppose we want to store an integer number 27, then it is best to use byte because it will reserve only 1 byte space in memory.
- If you use int data type then it will reserve 4 byte space in memory, so we are wasting memory.
Example
Output
short
It is also use to store an integer (whole number), it can store a bigger number than byte but smaller than int
- Size: 2 byte
- Range: -32768 to 32767
Example
Output
int
It is widely used data type for integer numbers ( whole number ), let’s see its size and range with example.
- Size: 4 byte
- Range: -2147483648 to 2147483647
Example
Output
long
If we have to store a very big value which is bigger than int range, in this case you can use long data type to store your integer value.
- Size: 8 byte
- Range: -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,808
- Note that you should end the value with an "L"
Example
Output
Decimal (number with deciaml point)
Decimal number is a number which contain decimal point (.), for example 345.5, 3827.726 etc., In java programming there are two data type which can be used to store a decimal value.
float
It is used to store a decimal number ( fractional number ) with 6 digit precision, here precision means digit after decimal point(.) .
- Size: 4 byte
- Range: 3.4e−038 to 3.4e+038
- It is good practice to end value with a "f".
Note: Precision means digits after decimal point, less precision digits less accurate value, bigger precision digits means more accurate value.
Example
Output
double
It is also used to store a fractional number with more accuracy, it uses precision upto 15 digits.
- Size: 8 byte
- Range: 4.9e−324 to 1.7e+308
- It is good practice to end value with a "d".
Example
Output
Scientific Numbers
In range of float and double we have used scientific number representation with “e”, where "e" indicates power of 10, for example 13e4 means 13* 104 which is equal to 130000. We can also use scientific numbers in programming, Let's see in example.
Example
Output
float or double..?
Both data types have their importance, if we want some less accuracy in result we should use float data type because its off six digits precision, for example in case of money we can use float because in money counting 2 digit of precision is enough like $45.37, $2.82, $103.50 etc.
double data type preferred in scientific calculation because, it offer 15 digits of precision and it supposed to more safe than float data type. So where precision is more valuable then always prefer to use double data type.
char data type
char: data type is used to store a single character form keyboard, the value must be surrounded by single quotes, for example ‘M’, ‘m’, ‘A’ etc. we can also use ASCII value as character variable value, let’s see in example.
Example
Output
Note**: In above example, Used two ASCII numbars 65 and 106, where the value of ASCII number 65 is 'A' and 106 is 'j'
boolean data type
To declare Boolean data type we use boolean keyword and it store a single value either try or false.
Basically boolean data type is used in condition testing to know whether condition is true or false. We will understand it in grate details in upcoming chapter.
Example
Output
Non-Primitive Data Types
These are identifiers, memory size is not pre-defined.
In other words non-primitive data types are derived from primitive data types means non-primitive data types are designed with the help of primitive data type, for example String data type, it is a group of character data type.
Non-primitive data types are also called as reference types because they refer to object. Below we have listed some widely used non-primitive data types.
- String
- Array
- Classes
- Interface, etc...
String
String is a non-primitive data type, it is used to store group of characters. The value must be surrounded by double quotes, for example “ Hello I am new in Java”.
Example
Output
Difference between Primitive & Non-Primitive
There are many differences between Primitive and Non-Primitive data types, lets know what they are.
- Primitive data types are keywords where as Non-Primitive data types are identifiers.
- Primitive data types are predefined by java where as Non-Primitive data types are defined by developer means they are not pre-defined except String.
- Primitive data types do not have addition methods where as Non-Primitive data types have additional methods.
- Primitive data types reserve predefined fixed memory size in RAM when they declared where as Non-Primitive data types are variable size.
- Primitive data types are start with a lowercase letter where as Non-Primitive data type start with uppercase letter.
- Primitive data types always contain a value where as Non-Primitive data types can be null.